ELEVATING THE NORM towards a world of climate resilience and sustainability.
The IFC Methodology establishes the new benchmark for quantifying, certifying, and optimizing the impact of climate and development goals.
ELEVATING THE NORM towards a world of climate resilience and sustainability.
The IFC Methodology establishes the new benchmark for quantifying, certifying, and optimizing the impact of climate and development goals.


IFC methodology strives to prevent harmful impacts on the environment while also acknowledging the positive effects of primary forests. The proposed shift in approach involves not only addressing the costs of land exploitation but also focusing on the positive outcomes of preserving environmental assets. The methodology aims to quantify these assets economically, enabling negotiations with landowners to ensure the conservation of these resources for the benefit of society.
Enhance the quality and standard of living for families in Native Communities by respecting and supporting their unique forms of production, social organization, cultural values, and beliefs.
IFC StandardMethodology
The goal is to strengthen self-management, collective well-being, good living, and community control over resources, all within a framework of harmonious and sustainable development.
UN HabitatSDGs
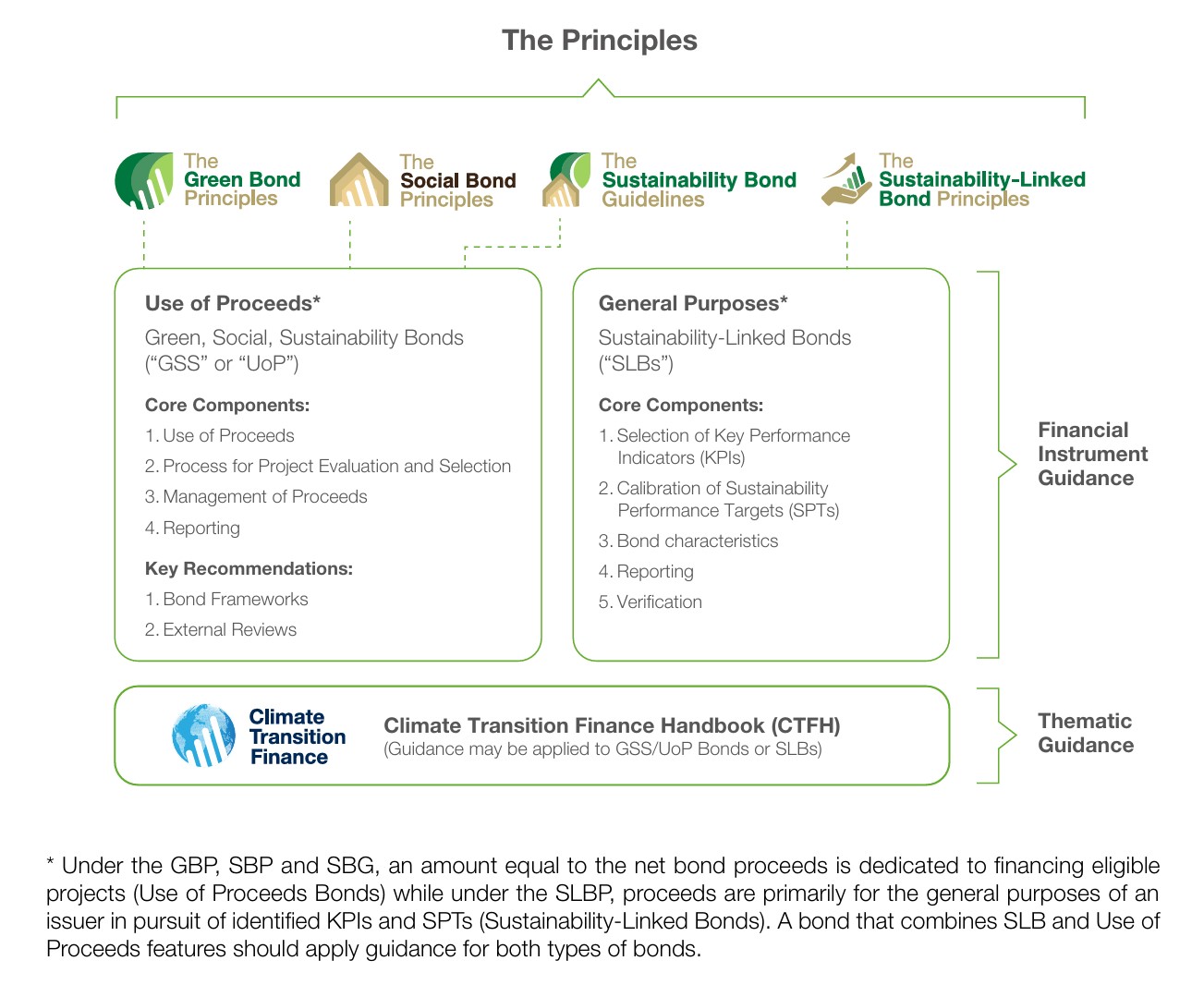
Green, Social and Sustainability Bonds are any type of bond instrument where the proceeds will be exclusively applied to eligible environmental and social projects or a combination of both.
The Clean Development Mechanism (CDM), as outlined in Article 12 of the Protocol, offers a pathway for countries with emission-reduction or emission-limitation commitments under the Kyoto Protocol (Annex B Party) to execute emission-reduction initiatives in developing nations. These projects have the potential to generate transferable Certified Emission Reduction (CER) credits, each equivalent to one tonne of CO2, which can be applied towards achieving Kyoto targets. Regarded by many as a pioneering initiative, the CDM is the first global environmental investment and credit scheme of its kind, offering a standardized emissions offset instrument, CERs.
The mechanism promotes sustainable development and emission reductions, while providing industrialized countries with some flexibility in how they achieve their emission reduction or limitation targets. In this context, the IFC standards play a crucial role in ensuring the integrity and effectiveness of these projects, fostering innovation, and introducing new types of credits for emission reduction and removal to the market.
Biomassa acima do solo de um ecossistema de “campina” em Roraima, norte da AmazoDnia brasileira. Acta Amazonica, v. 34, p. 577-586, 2004
Global warming and tropical land-use change: greenhouse gas emissions from biomass burning, decomposition and soils in forest conversion, shifting cultivation and secondary vegetation. Climatic change, v. 46, n. 1-2, p. 115-158, 2000
QuantificaçaHo do serviço ambiental do carbono nas florestas amazoDnicas brasileiras. Volume 12, Pags. 743-756, 2008
DeterminaçaHo do potencial de sequestro de carbono na recuperaçaHo de matas ciliares na regiaHo de SaHo Carlos-SP. 2004.
Pericles et al. O estado da arte na estimativa de biomassa e carbono em formaçoHes florestais. Chronicle, v. 5, n. 3, p. 220-224, 1982
Estoque e crescimento em volume, biomassa,carbono e dioxido de carbono em Floresta Estacional Semidecidual.” Revista AArvore, v. 35, p. 1277-1285, 2011
Ganaderí a bovina y cambio climatico en las Ame>ricas. Hacia modelos de desarrollo bajos en carbono. 2023
The technical and policy team at IFC is composed of globally acknowledged pioneers in the forestry and industrial domains. They are renowned for their profound knowledge and proficiency in carbon accounting and verification techniques.